MNDB Scheme Data Snapshot Jul–Dec 2024
Read the document below or download it here: MNDB Scheme Data Snapshot Jul–Dec 2024
About this document
Part 6A of the Privacy and Personal Information Protection Act 1998 (PPIP Act) established the Mandatory Notification of Data Breaches Scheme (MNDB Scheme), which requires public sector agencies to notify the Privacy Commissioner and affected individuals in the event of an eligible data breach involving personal or health information that is likely to result in serious harm. The MNDB Scheme commenced on 28 November 2023.
The Information and Privacy Commission (IPC) publishes quarterly statistical information on the number of eligible data breach notifications received under the MNDB Scheme. This snapshot is intended to provide agencies and the public with key summary data for the six-month period between July and December 2024.
The Privacy Commissioner will also publish the January – June 2025 Data Snapshot and an annual Trends Report for the full 2024–25 financial year.
Data Notes
Statistics in this report are current as of November 2025.
Percentages in some charts may not total 100% due to rounding.
The reported cause of a data breach is based on information provided by the reporting agency. In some instances, more than one cause has been identified by the agency. As a result, percentages for relevant charts may total more than 100%.
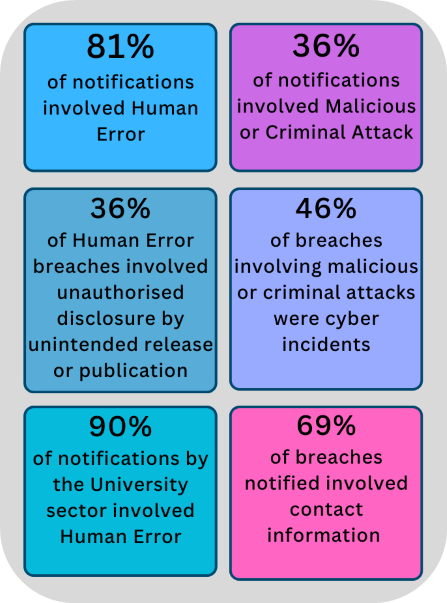
Summary of key findings
Key findings for the 01 July to 31 December 2024 reporting period:
Sector Snapshot
This table provides data on key metrics for each of the sectors which have notified data breaches during the reporting period.
|
|
Government |
Local Government |
University |
Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Number of notifications |
43 |
11 |
10 |
64 |
|
% of data breaches caused by human error |
81% |
73% |
90% |
81%[1] |
|
% of data breaches caused by criminal or malicious attack |
37% |
45% |
30% |
36%[2] |
|
% of data breaches with multiple causes |
19% |
27% |
20% |
20% |
|
Number of affected individuals |
55,330 |
6,041 |
477,576 |
539,292 |
1. Causes of data breaches
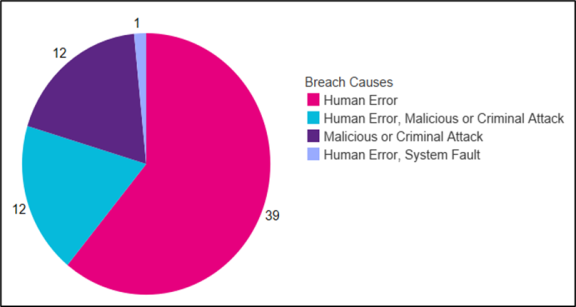
Figure 1: Number of notifications by cause of breach
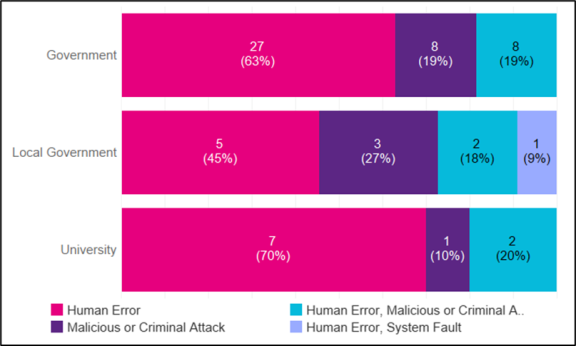
Figure 2: Number of notifications by cause of breach per sector
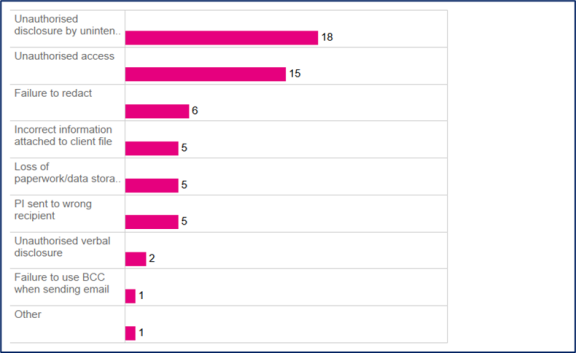
Figure 3: Number of notifications by cause of breach – Human Error
Data in this table reflects the cause selected by the agency in its notification to the Privacy Commissioner. Agencies may select more than one cause. Therefore, the total number reflected above is greater than the number of notifications shown in Figures 1 and 2 above.
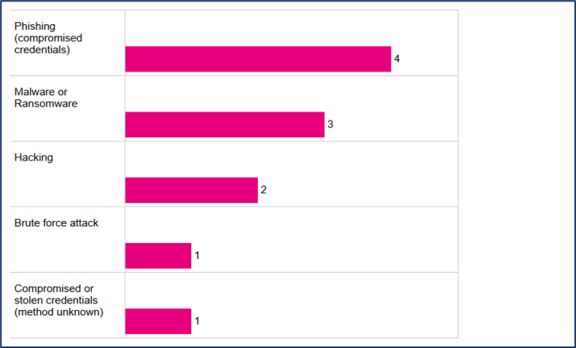
Figure 4: Number of notifications by cause of breach – Malicious or Criminal Attack
Data in this table reflects the cause selected by the agency in its notification to the Privacy Commissioner. Agencies may select more than one cause. Therefore, the total number reflected above is greater than the number of notifications shown in Figures 1 and 2 above.
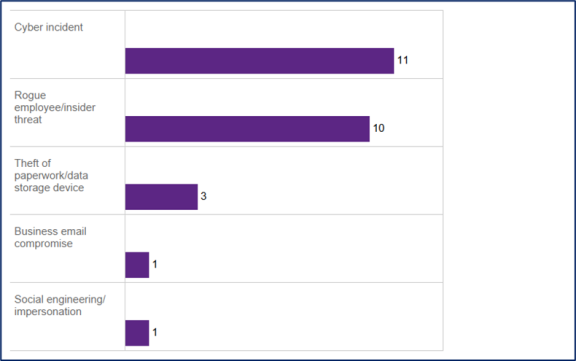
Figure 5: Cyber incident breakdown
Data in this table reflects the cause selected by the agency in its notification to the Privacy Commissioner. Agencies may select more than one cause. Therefore, the total number reflected above is greater than the number of notifications shown in Figures 1 and 2 above.
2. Type of personal information involved
Figure 6: Number of notifications by type of personal information
Data in this table reflects the categories selected by the agency in its notification to the Privacy Commissioner. Agencies may select more than one category. Therefore, the total number reflected above is greater than the number of notifications shown in Figures 1 and 2 above.
[1]This total includes data breaches caused solely by human error and breaches where human error was one of multiple causes responsible for the breach.
[2] This total includes data breaches caused solely by criminal or malicious attack and breaches where criminal or malicious attack was one of multiple causes responsible for the breach.